Hepatitis B - Vaccine
Hepatitis B virus
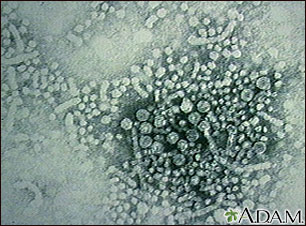
Hepatitis B is also known as serum hepatitis and is spread through blood and sexual contact. It is seen with increased frequency among intravenous drug users who share needles and among the homosexual population. This photograph is an electronmicroscopic image of hepatitis B virus particles. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Hepatitis B

The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for healthcare workers, people who live with someone with hepatitis B, and others at higher risk. The hepatitis B virus can damage liver cells. Immunization is also recommended for all infants and unvaccinated adolescents.
The Hepatitis B - vaccine protects against hepatitis B, a serious disease that damages the liver.
VACCINE INFORMATION
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the recommended childhood immunizations. Hepatitis spreads through contact with the blood and body fluids of an infected person. Hepatitis B can be passed from mother to baby during birth.
IMMUNIZATION SCHEDULE
Hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three injections (shots). The first shot is given to infants shortly after birth. All 3 doses are necessary for the most effective and longest lasting immunity.
If the mother of the infant carries the hepatitis B virus (HBV) in her blood, the infant needs to receive the first shot shortly after birth. The next two shots are given at 2 months of age and then at 6 months of age.
If the mother of the infant does not have signs of the HBV in her blood, the infant may receive the shot anytime before leaving the hospital, or the vaccine may be delayed until the 4 or 8 week visit to the primary care provider. If given shortly after birth, the second shot is given at 1 to 2 months and the third at 6 months.
For infants who do not receive the first shot until 4 to 8 weeks, the second shot is given at 4 months and the third at 6 to 16 months. In either instance, the second and third shots are given along with other routine childhood immunizations.
Adolescents who have not been vaccinated should begin the hepatitis B vaccine series at the earliest possible date.
SIDE EFFECTS
Most infants who receive the HBV vaccine have no side effects. Others may have minor problems, such as soreness and redness at the injection site or a mild fever. Serious problems are rare and are mainly due to allergic reactions to a component of the vaccine.
No comments:
Post a Comment