Heart Failure
Heart, section through the middle
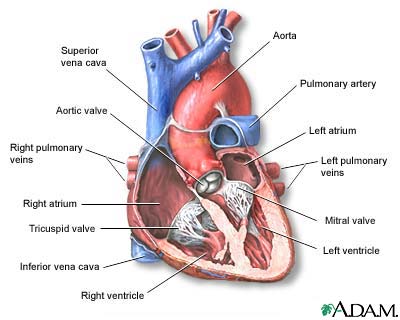
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
Heart, front view
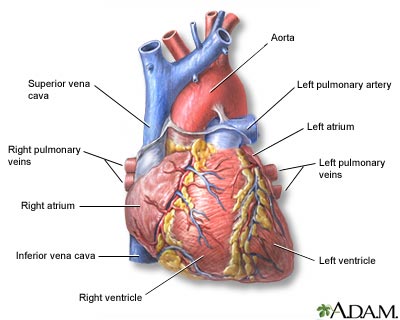
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Circulation of blood through the heart

The heart is a large muscular organ which constantly pushes oxygen-rich blood to the brain and extremities and transports oxygen-poor blood from the brain and extremities to the lungs to gain oxygen. Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the body's tissues through the aorta.
Heart failure, also called congestive heart failure, is a life-threatening condition in which the heart can no longer pump enough blood to the rest of the body.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Heart failure is almost always a chronic, long-term condition, although it can sometimes develop suddenly. This condition may affect the right side, the left side, or both sides of the heart. As the heart's pumping action is lost, blood may back up into other areas of the body, including: With heart failure, many organs don't receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which damages them and reduces their ability to function properly. Most areas of the body can be affected when both sides of the heart fail. The most common causes of heart failure are hypertension (high blood pressure) and coronary artery disease (for example, you have had a heart attack). Other structural or functional causes of heart failure include the following: Heart failure becomes more common with advancing age. You are also at increased risk for developing heart failure if you are overweight, have diabetes, smoke cigarettes, abuse alcohol, or use cocaine. Symptoms Infants may sweat during feeding (or other exertion). Some patients with heart failure have no symptoms. In these people, the symptoms may develop only with these conditions: A physical examination may reveal either an irregular or a rapid heartbeat. There may be distended neck veins, enlarged liver, swelling of the limbs (peripheral edema), and signs of fluid around the lungs (pleural effusion). Listening to the chest with a stethoscope may reveal lung crackles or abnormal heart sounds. Blood pressure may be normal, high, or low. An enlargement of the heart or decreased heart functioning may be seen on several tests, including the following: This disease may also alter the following test results: If excessive fluid has accumulated around the sac surrounding the heart (pericardium), you may need to have the fluid removed through a pericardiocentesis. If you have heart failure, your doctor will monitor you closely. This means having follow up appointments at least every 3 to 6 months, figuring out any underlying cause and treating it, and periodic testing of your heart function. For example, an ultrasound of your heart, called an echocardiogram, will be done once in awhile to give an estimate of how well your heart is pumping blood with each stroke or beat. It is also your responsibility to carefully monitor yourself and help manage your condition. One important way to do this is to track your weight on a daily basis. Weight gain can be a sign that you are retaining fluid and that the pump function of your heart is worsening. Make sure you weigh yourself at the same time each day and on the same scale, with little to no clothes on. Other important measures include: Here are some tips to lower your salt and sodium intake: Your doctor may consider prescribing the following medications: Sometimes, hospitalization is required for acute CHF. Hospitalized patients may receive oxygen and intravenous medications such as vasodilators and diuretics. Medicines such as nesiritide (Natrecor) help dilate blood vessels and may also be helpful. Medicines called inotropic agents help improve the heart's ability to pump blood. Such drugs include dobutamine and milrinone. They are given by IV. Unstable patients receiving several medications usually need also hemodynamic monitoring with Swan-Ganz catheterization. Severe cases of CHF require more drastic measures. For example, excess fluid can be removed through dialysis, and circulatory assistance can be provided by implanted devices such as the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) and the left ventricular assist device (LVAD). These devices can be life-saving, but they are not permanent solutions. Patients who become dependent on circulatory support will need a heart transplant. A number of studies have shown that heart failure symptoms can be improved with a special type of pacemaker. It paces both the right and left sides of heart. This is referred to as biventricular pacing or cardiac resynchronization therapy. Ask your provider if you are a candidate for this. eart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Many forms of heart failure can be controlled with medication, lifestyle change, and correction of any underlying disorder. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
Signs and tests
Complications
Possible side effects of medications include:
Prevention
Follow your health care provider's recommendations for treatment of conditions that may cause congestive heart failure. These recommendations may include: Also, consider the following lifestyle habits, especially if you have a strong family history of CHF:
References
Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, et al. ACC/AHA 2005 Guideline Update for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:1-82.
No comments:
Post a Comment