Heart-and-Lung Transplant
Lungs
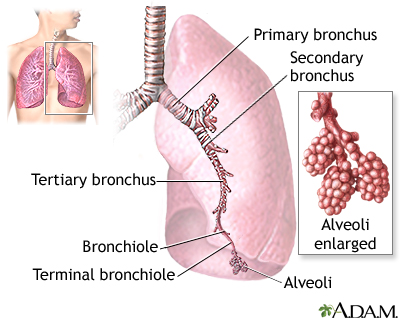
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Thoracic organs
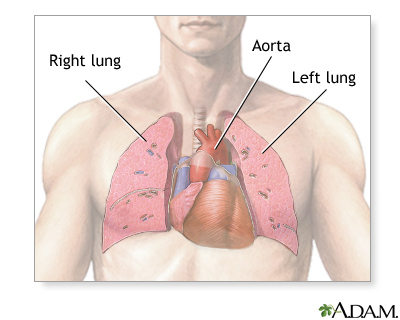
The thorax is also called the chest and contains the main organs of respiration and circulation. The heart through its main artery, the aorta, pumps oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. The lungs provide oxygen to the cells of the body and eliminate carbon dioxide. Together these organs sustain some of the most critical life functions of the body.
Heart-lung transplant - series: Normal anatomy
 |
Heart-and-lung transplant is surgery to replace a diseased heart and lungs with a healthy heart and lungs from a human donor.
Description
Heart-and-lung transplant operations have been performed since 1980 in the United States. Since 1995, between 30 and 70 heart-lung transplants are performed each year, according to the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS).
The donated heart and lungs are from a person who has been declared brain-dead, but remains on life-support. Tissue matching helps find the best match of donated organs to the patient.
While the patient is deep asleep with general anesthesia, a cut is made through the breast bone. A heart-lung bypass machine takes over the circulating of the blood, and maintains oxygen levels to the body.
The patient's heart and lungs are removed, and the donor heart and lungs are stitched into place. The heart-lung bypass machine is disconnected. The blood flows through the donor heart and air flows in and out of the donor lungs.
Indications
Heart-lung transplant may be recommended for patients with:- Severely diseased lungs, such as with primary pulmonary hypertension
- Severely damaged heart
Heart-and-lung transplants are not recommended for patients who have poor kidney or liver function, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, or other serious diseases.
Risks
Risks for any anesthesia are:
Risks for any surgery are:
Additional risks of transplant includes:
Expectations after surgery
A heart-and-lung transplant extends the life of a patient who would otherwise die. The operation is done only when there is a very good chance of success. While long-term outcomes are unknown at this time, 5-year survival is about 40 - 50%.
As with all major organ transplants, the problems are finding a donor, preventing rejection, and the cost of the surgery and medications.
Finding a donor for heart-lung transplant can be difficult. The donated organs must come from a person who has been declared brain-dead, but is still on life-support. The patient who needs the transplant must be healthy enough to survive the surgery.
Preventing rejection is an ongoing process. The body's immune system considers the transplanted organs as invaders, and fights them.
To prevent rejection, organ transplant patients must take anti-rejection drugs such as cyclosporine and corticosteroids that reduce the body's immune response. These drugs also reduce the body's natural ability to fight off various infections.
No comments:
Post a Comment